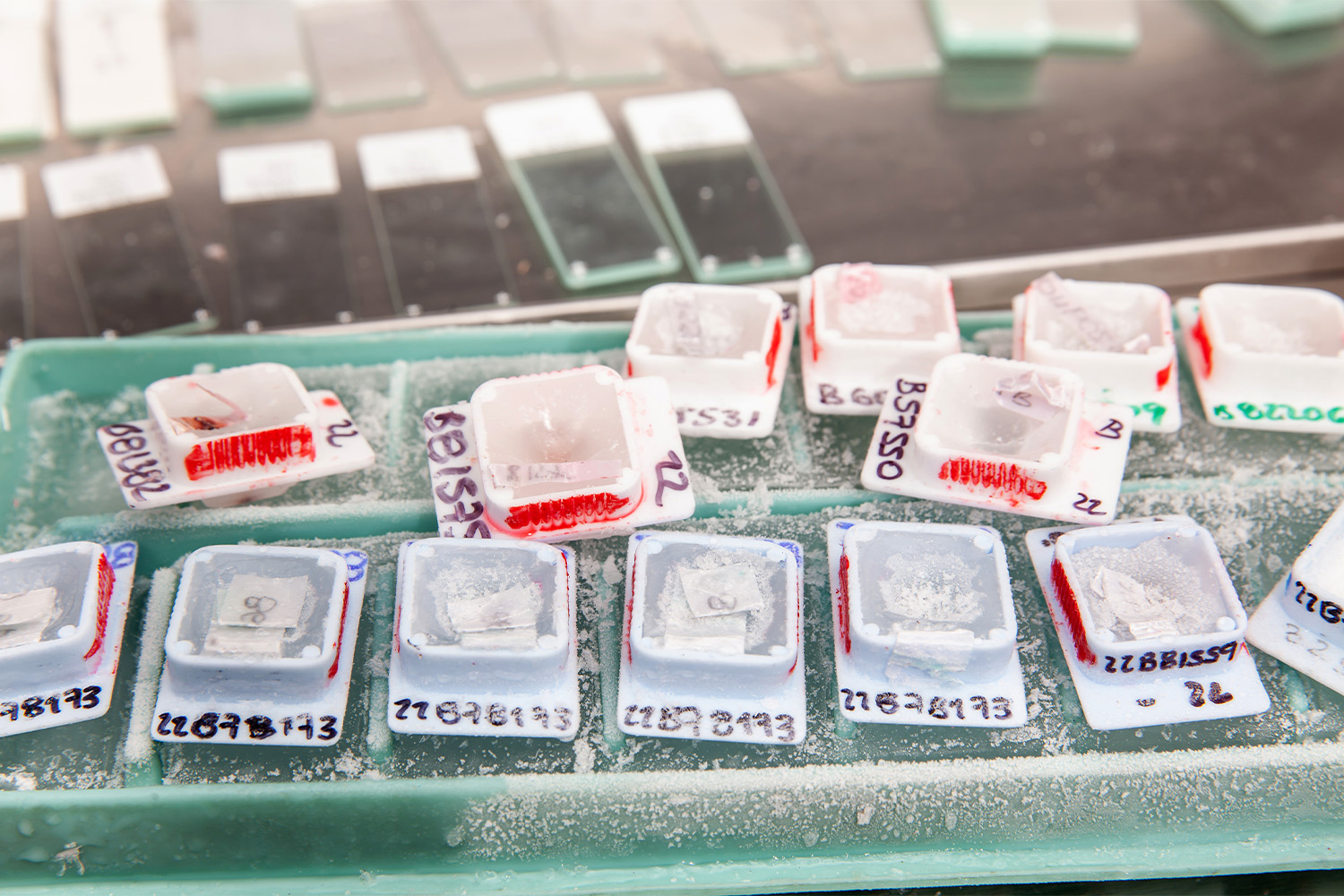
Fresh frozen tissue samples are used in clinical research to gain insight into various disease states. These samples provide researchers with invaluable information regarding the health of the patient, as well as providing a source of biomarkers and other data which can be used to develop targeted treatments.
Fresh frozen tissue samples are either obtained from a donor patient or created by centrifuging blood samples and then quickly freezing the resulting plasma at a low temperature in order to preserve its integrity. This allows the samples to be stored for extended periods of time without degradation, making them a valuable tool for clinical research.
Utilizing fresh frozen tissue samples for clinical research is a method of collecting data that has been used for many years. There are numerous advantages to this method of sample collection, including the ability to collect a large number of samples quickly and efficiently, as well as the ability to study samples in a variety of ways due to retaining the initial anatomy of the specimen.
Frozen tissue samples also provide a more accurate representation of the original sample than other methods and are generally more useful for liquid samples such as blood or urine samples.
Fresh frozen tissue samples are often a preferred method of collecting data for clinical research when compared to FFPE (formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded) samples.
Fresh frozen samples offer a variety of advantages, including better quality and consistency of data, improved preservation over time, and more efficient processing.
Additionally, frozen tissue samples allow for the collection of better-quality biological markers, genetic information such as DNA and RNA, and other data that can be used to create targeted treatments.
In contrast, FFPE samples are limited in scope, as they require the fixed tissue to be cut and stained before any research can be done.
Fresh frozen tissue can be more costly to acquire and usually is obtained in lesser quantities when compared to FFPE samples. However, biobanking, or storing tissue samples in large quantities in one location, has become a common practice that can facilitate the acquisition of many different types of specific tissue samples.
Transport logistics, sample type selection, and histologic characterization should all be considered when choosing to use a biobank for fresh frozen tissue samples in clinical research.
When it comes to finding a fresh frozen tissue provider, choosing to go with an established partner with extensive networking can make all the difference in a research endeavor.
At iProcess Global Research, you can expect to benefit from a network of over 1,000 sites globally with over 100,000 biospecimens shipped.
Fresh frozen tissue samples can sometimes be technically and logistically demanding to acquire, but iProcess has a track record of delivering results from the most simple to the most complex protocols required by clients.
Contact iProcess or request a quote today to learn more about fresh frozen tissue samples.
Sources:
Fresh frozen tissue: RNA extraction and quality control | PMC
Biobanking of fresh frozen tissue: RNA is stable in nonfixed surgical specimens | PMC