Obtaining quality, affordable biospecimens can quite often be a financially limiting component of any research. Knowing where to look for the most appropriate, inexpensive, and quality biospecimens is key when trying to obtain tissue samples in a large market of available biospecimen providers.
Finding the right, cost-effective source of tissue samples for research depends on the type of research being performed as well as the tissue sample itself.
Where Can We Find Tissue Samples?
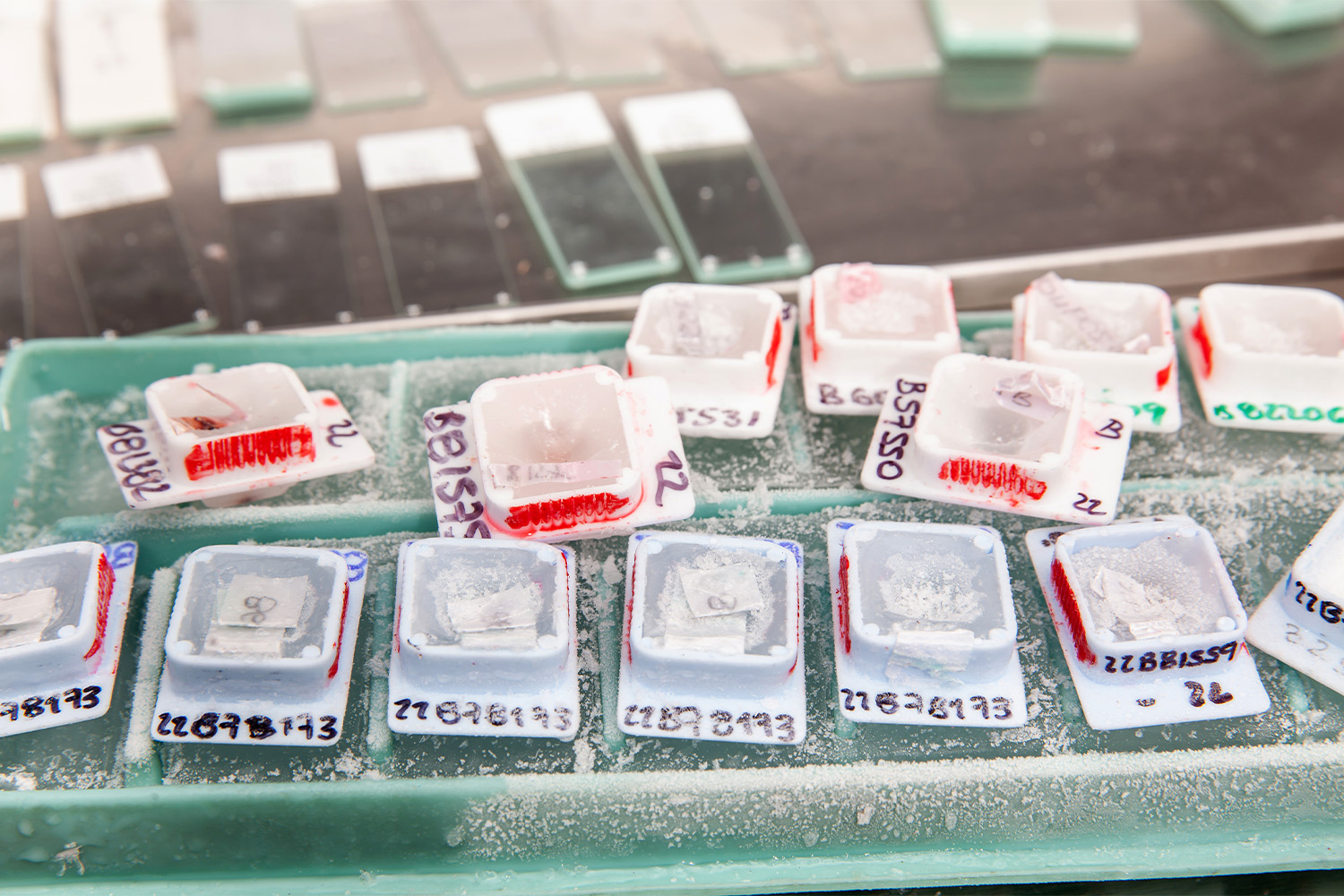
Human tissue specimens are not only useful at the time of diagnosis and treatment but can be useful for disease research going forward. Only a small proportion of surgical tissue acquisition is utilized for diagnosis or treatment, while the larger majority is stored in specialized surgical specimen biorepositories.
The stored tissues are either frozen or preserved and embedded in paraffin wax that allows the tissue to be useful for ongoing research in the future. One example of a large biorepository model is the Cooperative Human Tissue Network (CHTN), where tissues are explicitly provided to an investigator’s request.
Alternatively, tissues can be requested from tissue banks such as the National Cancer Institute Clinical Cooperative Group Banks.
Biobanks support scientific knowledge by allowing different professional figures of a variety of backgrounds and expertise the opportunity to obtain and collect biological and clinical data from human subjects. Subsequently, biobanks preserve the human and legal rights of each person that offers biomaterial for research.
Undoubtedly, biospecimens and biospecimen resources are fundamental to research and precision medicine in modern healthcare.
To learn more about biospecimens and biorepositories, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) provides the Biorepositories and Biospecimen Research Branch (BBRB) that provides leadership, tools, resources, and policies in biobanking for the global medical research community.
The Importance and Cost of High-Quality Biospecimens
Biomedical research depends on the availability of high-quality biospecimens. There is no replacement for specimens taken directly from the body. Many living tissue samples retain a physiological response to external stimuli they encounter, such as introduction to hot or cold temperatures, or even a potential chemotherapeutic.
As advocacy groups are trying to raise awareness of the importance of quality biospecimen donation, biospecimen suppliers are trying to keep up with demand.
Maintaining a high-quality biospecimen repository is associated with high cost. Implementing strict standard operating procedures for biospecimen harvesting translates to higher costs, and there may be a need for federal economic support to fund a high-level, comprehensive biobank.
What Tissue Procurement Method Is Right for Me?
Depending on the type of research being performed, the necessary type of tissue sample, and the research budget, the method of tissue sample obtainment may vary greatly:
The Cooperative Human Tissue Network
Prospective acquisition involves knowing exactly what type of specific tissue is desired prior to the sample being obtained. The CHTN repository can be useful in situations when a tissue sample needs to be tailored to exact research needs, such as biomarker-specific tumor samples of a given stage or age.
These samples go through the same quality control standards to ensure researchers attain the best samples.
A major advantage of the CHTN repository is the NCI’s grant support system that allows researchers at academic, government, and non-commercial entities access to samples by special request but for minimal cost. Besides a processing fee, this route may be the most viable for certain researchers.
A drawback can be that the CHTN is not a biospecimen storage bank, and therefore it does not have a catalog of available tissue samples. The CHTN also prioritizes researchers that are performing peer-reviewed research at non-profit or academic research centers over for-profit or commercial companies.
Regarding tissue samples specifically, the CHTN does provide tissue microarray (TMA) slides with limited pertinent clinical information. These slides may be useful as a research supplement or simply as a preliminary screening tool. Unfortunately, the CHTN does not custom fabricate TMA blocks for individual research projects.
Biospecimen Storage Banks
Researchers have access to numerous biospecimen marketplaces and distributors in today’s online, interconnected world. Many of these banks have access to millions of banked and clinically remnant samples that would be suitable for many kinds of research.
Unlike CHTN’s perspective, storage banks possess many tissue samples spanning a variety of species and disease states.
Initially, biobanks were founded locally and served a primary purpose for specific research projects, eventually growing in scale and decentralizing to meet growing demand. Today, biobanking permits large-scale analysis for specific disease biomarkers utilizing large amounts of biological data.
Technological advancements in combination with more precise and purposeful biospecimen collection have resulted in immensely diverse, sustainable, and plentiful biobanks across the globe.
Sometimes research demands a large volume of samples with wide-ranging diversity, and it is this type of scenario when storage banks play a sizable role. Frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue blocks are all commonly available from several companies.
FFPE tissue blocks are an often-disregarded source of tissue sampling, but because they are obtained regularly as part of a patient’s treatment due to the presence of relevant biomarkers, they are readily accessible and do not require frozen storage.
These samples offer immensely important clinical information in general research aside from treating the patient they were obtained from. Oncology, hematology, and immunology academic research or drug discovery can all benefit from instituting FFPE tissue blocks.
What Are Some Other Methods of Obtaining Tissue Samples?
Minimally Invasive Tissue Samples
Minimally invasive tissue samples (MITS) refer to relatively new technology for obtaining tissue specimens using fine needle biopsies that are suitable for laboratory analysis. The benefit of using MITS is mostly reflected in underserved parts of the world without access to healthcare systems to perform a proper autopsy.
Mostly a public health and epidemiological tool, MITS is a potentially more feasible option for a diagnostic autopsy that is less disfiguring and requires fewer resources compared to a complete diagnostic autopsy.
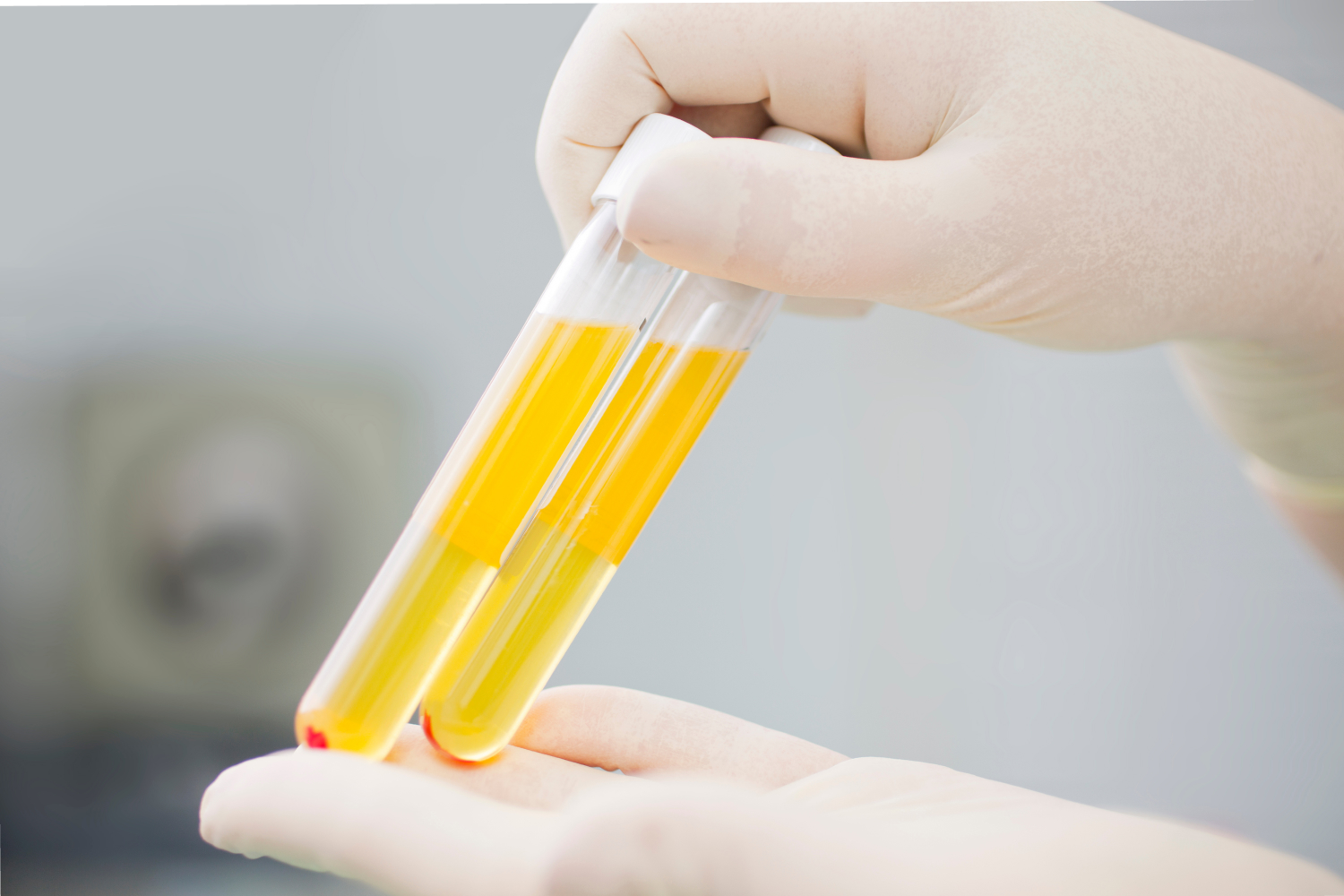
Liquid Biopsy
A liquid biopsy is a simple, non-invasive blood draw that can reveal similar information to a surgical biopsy, such as the presence of a cancer cell mutation. Information provided by liquid biopsy is as valuable as a regular biopsy in some disease states because it can give diagnostic clues about which treatments are most likely to work in some patients.
Unfortunately, liquid biopsy is only available for select types of cancer mutations and is not widely utilized.
Summary
The importance of the ability for researchers to access biospecimens to further research of diseases, promote drug discovery, and advance our utilization of diagnostics cannot be understated.
Assessing tissue cell structure and determining individual cell biomarkers to diagnose and predict the most effective treatment modality will continue to rapidly change the way we implement more personalized medicine.
Procuring tissue samples can be time-intensive and expensive, but finding the right source for biospecimens can make the process immensely easier. iProcess Global Research Inc is one such company that specializes in working with major pharmaceutical, diagnostic, and research organizations to produce a wide variety of biospecimen types in even the most complex collection protocols.
In addition, iProcess has the flexibility of providing liquid biopsies and both banked or prospective specimens to be tailored to exactly the research needs. Over the course of 17 years, iProcess truly has created a reputation as one of the industry’s best and most reliable sources of biospecimens.
Request a quote for free to receive a custom quote that is tailored to your research needs.
Sources
Biobanking In Health Care: Evolution And Future Directions | Journal Of Translational Medicine
Biobanking For Personalized Medicine | Advances In Experimental Medicine And Biology